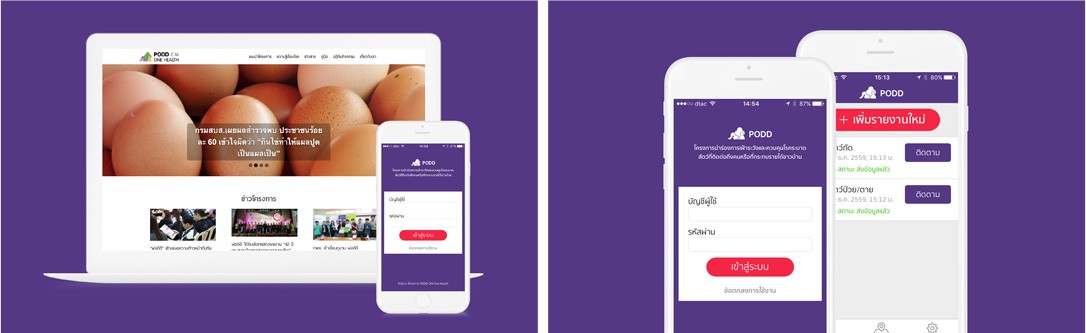
PODD
PODD – Participatory Onehealth Disease Detection is a pilot project on surveillance and control of zoonotic diseases that could possibly infect humans and cause economic losses to villagers. The project was initiated based on studies which showed that an effective disease surveillance system that is capable of controlling infectious diseases in both humans and animals in a timely manner would largely reduce both the health and economic costs of the villagers.
With a strong foundation of Lanna culture within the communities which emphasizes on close relationships and mutual support among villagers, the onehealth disease surveillance system can easily leverage on the community participation to prevent the spread of epidemic. In addition, the advancement in digital technology had significantly raised the efficiency of the system by enabling information exchanges in much shorter time and a wide geographical coverage.
The pilot was started as a collaboration study project involving the Chiang Mai provincial government and the communities in the province.
Problem & Concept
Epidemic claims thousands of lives every year and zoonotic diseases are especially lethal, for example Avian Flu, Swine Flu, HIV, and Ebola.
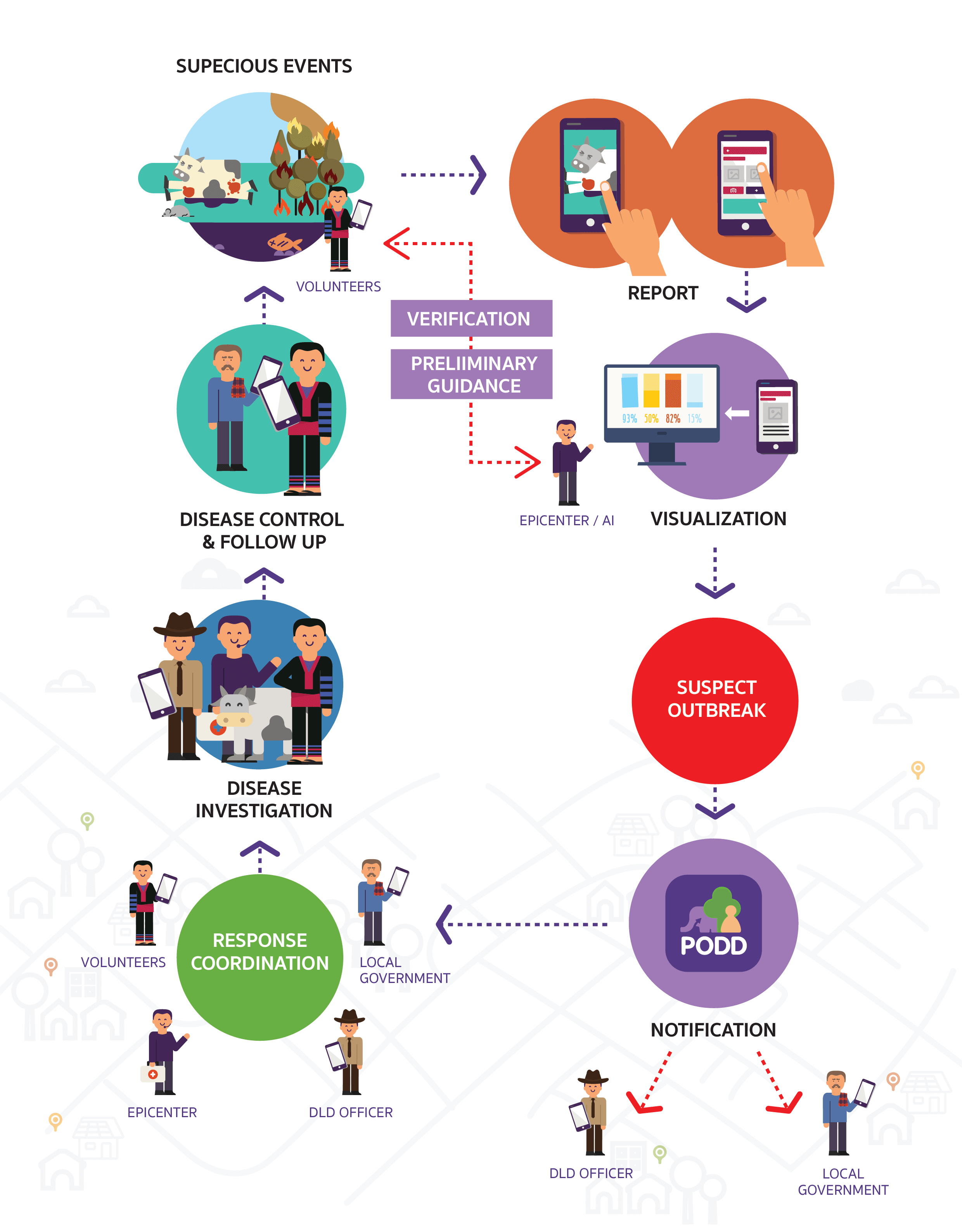
In some areas, humans and animals stay in close proximity which results in high chances of cross infection. The conventional way of epidemic control from validation of outbreak to implementation of control measures often takes long period of time, especially when animals are unable to report their own illnesses. By the time the epidemics are put under control, most of the time it has already incurred significant losses and damages.
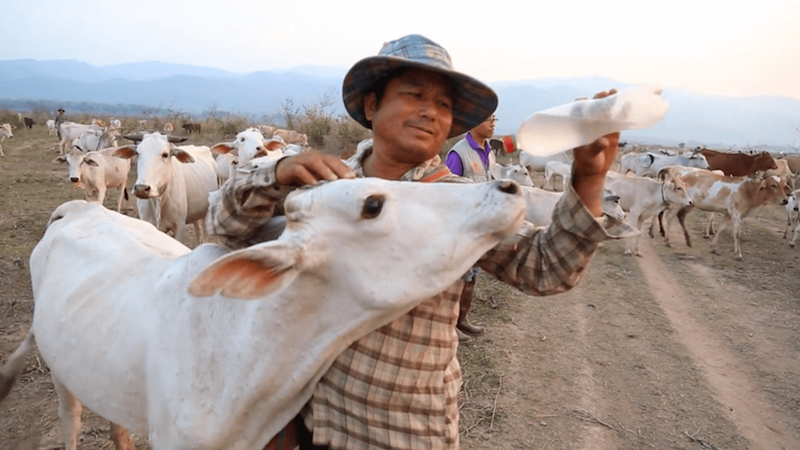


Would it be possible for us to stop epidemics even before they spread by setting up an effective surveillance system?Execution
PODD was initiated through the collaboration of experts from numerous disciplines, including veterinary science professors from Chiang Mai University, provincial livestock officers, public health officers, health professionals, economists, political scientists, provincial government officers, and volunteers. In addition, Skoll Global Threats Fund provided network and funding that helped the project make a head start and Opendream helped set up the technology platform to support multi-party real-time communication. The close-knit collaboration of multiple stakeholders with each party helping to control and monitor the part of the project that they are responsible for ensured the effectiveness and efficiency of the system.
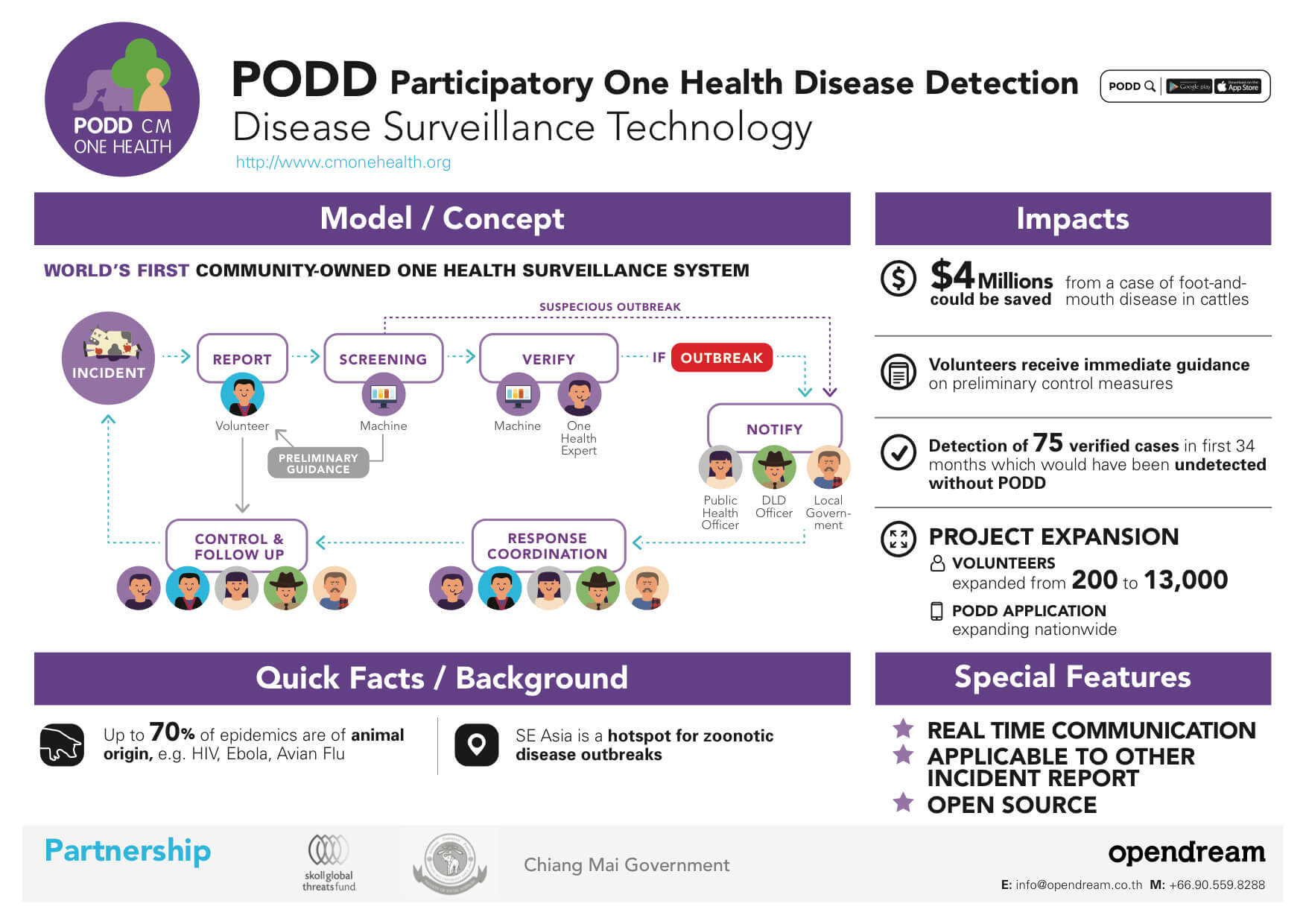
Impact
- The number of villagers who serve as PODD volunteers by helping to report suspicious disease outbreaks increased from 600 to 2,000.
- There had also been an increase in number of communities both in Chiang Mai province and surrounding provinces that apply the PODD system in monitoring disease outbreaks as well as other incidents, such as forest fire, unsafe consumer goods at the local markets and so on.
- In the first 34 months since the launch of the PODD system, a total of 75 outbreaks had been successfully stopped from spreading. Otherwise, the outbreaks could have caused up to millions baht loss in economic value.
- Through the PODD system, villagers in communities are empowered to detect and control disease outbreaks in their communities by themselves sustainably, reducing the reliance on centralized support.
- Furthermore, PODD is an open source program, which facilitates replication in other communities for disease surveillance or even other applications in future.